从DBus-cxx源码解析官方例程
Linus Benedict Torvalds 曾说 :“Read The F**king Source Code 🙂!”
该文章仅是个人学习的记录。例程代码来自dbus-cxx: Quick start example 0: A simple server and client
首先请先了解 DBus 的基本概念和大致框架再来阅读该文章,并自行从github中拉下一份 DBus-cxx的源码,配合 DBus-cxx 文档和源码注释阅读。文章并不会把所有涉及到的源码都贴出来,有很多省略部分,请自行查找对应源码阅读。源码 Releases 版本为 2.3.0。
server.cpp 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 #include <dbus-cxx.h> #include <unistd.h> double add (double param1, double param2) return param1 + param2; }int main () create ();create_connection (DBus::BusType::SESSION);if (conn->request_name ("dbuscxx.quickstart_0.server" , DBUSCXX_NAME_FLAG_REPLACE_EXISTING) != DBus::RequestNameResponse::PrimaryOwner)return 1 ;create_object ("/dbuscxx/quickstart_0" , DBus::ThreadForCalling::DispatcherThread);create_method <double (double , double )>("dbuscxx.Quickstart" , "add" , sigc::ptr_fun (add));sleep (10 );return 0 ;
create() 首先是第一句:
std::shared_ptrDBus::Dispatcher dispatcher = DBus::StandaloneDispatcher::create();
在官方文档 中可以找到 StandaloneDispatcher 这个类的介绍
creates a new thread that handles all of the reading and writing to the bus.
StandaloneDispatcher 这个类并不复杂。定位到 create 源码部分,可以看到 create 函数的实现其实是返回了一个StandaloneDispatcher 的类智能指针,且 is_running 的默认参数为 true
后面很多类的创建都是用类似的 create 方法实现,就不再赘述
1 2 3 std::shared_ptr<StandaloneDispatcher> StandaloneDispatcher::create ( bool is_running ) {return std::shared_ptr <StandaloneDispatcher>( new StandaloneDispatcher ( is_running ) );
在 StandaloneDispatcher 的构造函数中完成了初始化的内容
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 StandaloneDispatcher::StandaloneDispatcher ( bool is_running ) {make_unique <priv_data>();if ( socketpair ( AF_UNIX, SOCK_STREAM | SOCK_NONBLOCK, 0 , m_priv->process_fd ) < 0 ) {SIMPLELOGGER_ERROR ( LOGGER_NAME, "error creating socket pair" );throw ErrorDispatcherInitFailed ();if ( is_running ) { this ->start (); }
首先利用 socketpair 建立一堆匿名的嵌套字连接,使用的是管道流SOCK_STREAM连接,即建立的是双向通道,每一端都可以进行读写,并将套接字描述符分别放在process_fd[0] 和 process_fd[1] 中,然后调用 start() 开始线程.
结合源码不难分析出,DBus-cxx 中 process_fd[0] 是写端,process_fd[1] 是读端
在 start() 中利用 std::thread 开始线程,执行关键的线程函数 dispatch_thread_main
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 void StandaloneDispatcher::dispatch_thread_main () int > fds;for ( std::shared_ptr<Connection> conn : m_priv->m_connections ) {set_dispatching_thread ( std::this_thread::get_id () );while ( m_priv->m_running ) {clear ();push_back ( m_priv->process_fd[ 1 ] );for ( std::shared_ptr<Connection> conn : m_priv->m_connections ) {if ( !conn->is_registered () ) {bus_register ();push_back ( conn->unix_fd () );bool , int , std::vector<int >, std::chrono::milliseconds> fdResponse =wait_for_fd_activity ( fds, -1 );int > fdsToRead = std::get <2 >( fdResponse );if ( fdsToRead[ 0 ] == m_priv->process_fd[ 1 ] ) {char discard;if ( read ( m_priv->process_fd[ 1 ], &discard, sizeof ( char ) ) < 0 ){SIMPLELOGGER_DEBUG ( LOGGER_NAME, "Failure reading from dispatch thread process_fd: " strerror ( errno ) );dispatch_connections ();
关键点有以下几个
首先在while中能看到一个对 m_connection 的遍历,在执行create的时候 m_connection 中的数量为0,所以并不会进入 bus_register 阶段,这段代码中的 bus_register 就留到下一个语句中来解释。现在只需要知道这个for循环是用来遍历connection 把还没有没有注册的连接向bus中注册,获得 unique name。
首先看最后的 dispatch_connections()函数,这个函数调用 Connections::dispatch 方法写入和尝试读取bus的信息,并作处理。这样就实现了在线程循环中写入需要些的数据和从bus中读取数据。主要部分如下。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 DispatchStatus Connection::dispatch ( ) {flush ();readMessage ();process_single_message ();if ( m_priv->m_outgoingMessages.empty () &&empty () ) {else {return m_priv->m_dispatchStatus;
最后返回disptch的状态,如果还有消息数据残留,则在dispatch_connections()使用wakeup_thread 唤醒线程。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 void StandaloneDispatcher::wakeup_thread () char to_write = '0' ;if ( write ( m_priv->process_fd[ 0 ], &to_write, sizeof ( char ) ) < 0 ) {SIMPLELOGGER_ERROR ( LOGGER_NAME, "Can't write to socketpair?!" );
wakeup_thread() 在很多需要重复执行 dispatch_thread_main 的地方都用到了,那么是怎么做到的呢。我们需要回到线程函数的中间 wait_for_fd_activity(fds, -1) 。这个函数的作用就是等待给定fds的任何活动,比如读、写。那么执行线程函数的主循环时候,会停在这里等待其他地方对fds进行操作,并不会立刻处理消息的读写,然后再开始进入消息处理的流程。而 wakeup_thread 正是通过向 process_fd 写入一个 ‘0’ 从而达到了唤醒线程的功能。
至此,第一句语句的大概流程分析完毕,create() 函数的功能就是新建。
create_connection() 然后是 dispatcher->create_connection(DBus::BusType::SESSION) ,该函数用来创建Connection类实例。很简单,一共只有三句,但这三句都很关键,涉及到很多通信流程的准备和初始化,让我们来一句一句分析。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 std::shared_ptr<DBus::Connection> StandaloneDispatcher::create_connection ( BusType type ) {create ( type );bus_register ();if ( this ->add_connection ( conn ) ) { return conn; }return std::shared_ptr <Connection>();
首先第一句 Connection::create() ,利用 create 新建了一个 Connection 类,其构造函数简化如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 Connection::Connection ( BusType type ) {make_unique <priv_data>();if ( type == BusType::SESSION ) {char * env_address = getenv ( "DBUS_SESSION_BUS_ADDRESS" );if ( env_address == nullptr ) {return ;string ( env_address );SIMPLELOGGER_DEBUG ( LOGGER_NAME, "Going to open session bus: " + sessionBusAddr );open_transport ( sessionBusAddr );else if (){if ( !m_priv->m_transport || !m_priv->m_transport->is_valid () ) {SIMPLELOGGER_ERROR ( LOGGER_NAME, "Unable to open transport" );return ;
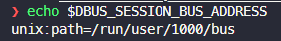
其中需要注意的是 getenv( "DBUS_SESSION_BUS_ADDRESS" ),我们可以在终端输入echo $DBUS_SESSION_BUS_ADDRESS , 获得如下输出,path=后面的就是 dbus-daemon 的地址。系统启动脚本中会调用 dbus-launch 来启动一个 dbus-daemon ,同时会把这个 dbus-daemon 赋予这个环境变量中。这个路径是一个socket类型文件。
在我的机器中,系统启动时对该环境变量的设定在 /etc/X11/Xsession.d/20dbus_xdg-runtime
然后再通过 Transport::open_transport 传入这个字符串并返回一个 Transport 类指针,并保存在 m_transport 中, 而在这个 Transport 的类中就包含了关键的 writeMessage 和 readMessage 方法,后续的读写操作都是调用这个类指针来完成。
在 open_transport 函数的开始调用解析函数 parseTransports 对这个字符串进行拆解。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 std::shared_ptr<Transport> Transport::open_transport ( std::string address ) {parseTransports ( address );if ( !path.empty () ) {open_unix_socket ( path, false );if ( fd >= 0 ) {create ( fd, true );if ( retTransport ) {priv::SASL saslAuth ( retTransport->fd(), negotiateFD ) ;bool , bool , std::vector<uint8_t >> resp =authenticate ();get <2 >( resp );if ( std::get <0 >( resp ) == false ) {SIMPLELOGGER_DEBUG ( LOGGER_NAME, "Did not authenticate with server" );reset ();
该函数并不难理解,具体代码自行查看源码,结果就是将上图中的 unxi:path=/run/user/1000/bus 解析为如下( 论正则的好处,C++居然还没有引入正则 ),这是DBUS_SECCSION_BUS_ADDRESS 只有一个值的情况,多值情况可以自己结合源码分析一下。
tmpTransportName = “unix”
然后将 tmpKey 和 tmpValue 保存到map对象tmpConfig 中,然后push_back 到retval中并返回。
知道 parseTransports 函数返回了什么,后面的就好理解了。
回到 open_transport 函数,后面调用了dbus-cxx 自己实现的 open_unix_socket 打开了这个dbus_daemon 路径,并返回fd,接下来的关键就在于重点就在于 retTransport = SendmsgTransport::create( fd, true ); SendmsgTransport 是 Transport 的子类,实际的writeMessage 和 readMessage 方法就是在这里实现的。
在官方文档中这个SendmsgTransport 的介绍是
回到 open_transport 函数,priv::SASL saslAuth( retTransport->fd(), negotiateFD ) 这句是生成一个 SASL 安全认证,然后与服务器进行身份认证。
SASL:Simple authentication and Security layer
然后是 conn->bus_register(); 对应源码如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 bool Connection::bus_register () if ( !m_priv->m_transport || !m_priv->m_transport->is_valid () ) {return false ;if ( is_registered () ) {return true ;create ( shared_from_this () );Hello ();return true ;
这个函数主要新建 DBusDaemonProxy 类指针,使用 shared_from_this 传递参数,然后在DBusDaemonProxy 构造函数中新建了很多方法,这里也可以看出 dbus-cxx 与 dbus 的联系
1 2 3 4 DBusDaemonProxy::DBusDaemonProxy ( ) {this ->create_method <std::string ()>( "org.freedesktop.DBus" , "Hello" );
而 create_method 定义在 objectproxy.h 中,具体作用可以看源码注释
Creates a proxy method with a signature based on the template parameters and adds it to the named interface
然后调用Hello方法返回 unique name 保存在m_priv中,也就是终端输入busctl 显示的那些以 : 开始的名字,这是 DBus 的功能,详情请跳转链接 。
然后回到 create_connection 中,看到 add_connection 部分,这个函数主要就是把连接加入到 dispatcher 中,可以看到 这个conection获取了 分发线程的线程id,然后还利用push back把connection压入 m_connection 中,最后唤醒线程,在 dispatch_thread_main 中执行连接的分发
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 bool StandaloneDispatcher::add_connection ( std::shared_ptr<Connection> connection ) if ( !connection || !connection->is_valid () ) { return false ; }set_dispatching_thread ( m_priv->m_dispatch_thread.get_id () );signal_needs_dispatch ().connect ( sigc::mem_fun ( *this , &StandaloneDispatcher::wakeup_thread ) );push_back ( connection );wakeup_thread ();return true ;
至此,create_connection 完毕
request_name() conn->request_name("dbuscxx.quickstart_0.server", DBUSCXX_NAME_FLAG_REPLACE_EXISTING)
request_name 比较简单,也就是获取一个bus名称,直接找到源码实现
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 RequestNameResponse Connection::request_name ( const std::string& name, unsigned int flags ) {if ( !is_valid () ) {throw ErrorDisconnected ();uint32_t retval = m_priv->m_daemonProxy->RequestName ( name, flags );switch ( retval ) {case DBUSCXX_REQUEST_NAME_REPLY_PRIMARY_OWNER:return RequestNameResponse::PrimaryOwner;
重点在于 m_priv->m_daemonProxy->RequestName( name, flags ) ,这里调用的是DBus的方法 RequestName ,从DBus 的官方文档中可以看到该方法是用来获取指定的bus名称,根据不同的flags有不同的效果
更多请参考 D-Bus 官方文档
第一部分结束